Gaskets have the main industrial uses: providing artistic and accurate sealing for various systems to avert leakages which could render the contamination unsafe or inefficient. Among the provided ranges of gaskets, metallic gaskets, especially semi-metallic and spiral wound ones, lie in their high range for their general lifetime in demanding environments. The article sinks into the life, construction, advantages, and application potentials of these types of metallic gaskets, thereby providing the supporting factors behind their indispensability in industries from petrochemical processing through power generation. Whether looking out for possibilities to ease your operations or to find their effect on service integrity, this guide will equip you with a handful of pertinent ideas on which you may decide.
Introduction to Gaskets

Gaskets form a vital component in sealing between two surfaces to prevent leakages from the system and maintain system integrity under certain circumstances. They are usually rubber gaskets, metal gaskets, or composite ones as per application requirements. Gaskets, in use, prevent fluid or gas leakage in automotive, manufacturing, aerospace, and other sectors where performance and safety are critical. Their functioning depends heavily on the appropriate material choice, proper installation, and material compatibility with operating conditions.
Definition of a Gasket
A gasket is a mechanical seal that fills the space between two or more mating surfaces under compression that prevents fluids or gases from escaping. A gasket artificially maintains the structural integrity of a system in many applications ranging from automotive engines to industrial machinery to aerospace. Usually, a gasket is made from rubber, silicone, metal, or composite materials based on factors such as temperature tolerance, chemical resistance, and pressure tolerance. Proper installation, compatibility with the operating environment, and suitability for the job at hand ensure a gasket’s lifespan and effectiveness.
Importance of Gaskets in Sealing
The importance of gaskets in sealing applications cannot be overstressed. Recent trending data acquired engine divulges many queries pertaining to “effective sealing solutions” and “industrial gasket types,” hinting at a rising sunset for reliable sealing systems in every industry across the globe. Gaskets prevent leaks, preserve the integrity of systems, and allow for safety in the act of operating. To illustrate, the oil and gas sectors, pharmaceutical production, and food industries rely on gaskets to observe stringent regulatory standards for containment and hygiene. In concert with improvements to gaskets-an evolution of materials and design, multi-layer composites, new resistance to extreme heat, and chemical attack-are going to further improve their efficacy. The technology application, therefore, is a clear sign of an industry-wide cry to heighten operational performance while equally trimming costs on maintenance and downtime, making gaskets indispensable in both conventional and emerging applications.
Overview of Gasket Types
When talking about different types of gaskets, I feel they would best be classified on a material basis or working principle. For instance, metallic, non-metallic, and composite gaskets with each suited for its specific application; metallic gaskets are highly durable and good for high-pressure environments, while non-metallic ones like rubber or PTFE are somewhat flexible and chemically resistant and suitable for low-pressure systems; composite gaskets made from a combination of materials provide a perfect balance between strength and adaptability. Each one is apt in a specific condition, and the choice depends mostly on working conditions and system requirements.
Metallic Gaskets
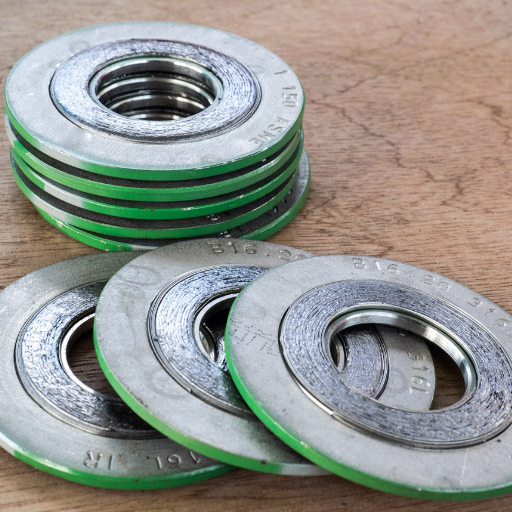

A metallic gasket can tolerate harsh conditions including extreme temperature and pressure. Common varieties are ring-type joint (RTJ) gaskets, corrugated metal, and spiral wound gaskets. Metallic gaskets provide good rigidity and strength. Typically, they occur in systems with high pressure and temperature; these include systems from oil and gas, chemical, and power-generation industries. Acceptable installation and compatibility of the flange materials for proper sealing must be assured.
Types of Metallic Gaskets
- RTJ Gaskets: Precision engineered and applied in high-pressure and temperature systems, guaranteeing a seal in the oil and gas or petrochemical industries
- Corrugated Metal Gaskets: Have a corrugated core, with a soft facing material layered on top, making them highly adaptable to imperfect flanges whilst providing excellent sealing under moderate pressures
- Spiral Wound Gaskets: Consist of metallic and filler materials mixed and coiled together, with remarkable ability and power to seal in pressure and temperature fluctuations
Each is chosen based on operating needs with the consideration of being compatible with the material of the flange and correctly installing it to achieve the highest performance of the gasket.
Applications of Metallic Gaskets
Metallic gaskets are extensively used in industries requiring strong and reliable sealing solutions for extreme working conditions. Typical applications would fall under:
- Oil gassing pipes
- Petrochemical plants
- Power generation facilities
- Aerospace systems
- Refineries and chemical processing plants
- Heat exchangers, motors, and boilers
These gaskets are also deployed in refineries and chemical processing plants to contain leaks of hazardous materials, maintaining safety and environmental standards. Furthermore, they find applications in heat exchangers, motors, and boilers where their durability through thermal cycles is paramount in maintaining system integrity.
Advantages of Using Metallic Gaskets
- Superior Durability: Very durable with superior sealing ability for high pressure and temperature applications
- Chemical Resistance: Having resistance to chemical attack, these gaskets secure a long time of use in harsh atmosphere such as refineries and chemical plants
- Thermal Cycling: They can withstand the effect of thermal cycling, maintaining their sealing integrity even under temperature changes
- Safety Enhancement: Preventing possible leakage of hazardous materials contributes to safety and fulfillment of high environmental standards’ regulatory standards
Semi-Metallic Gaskets
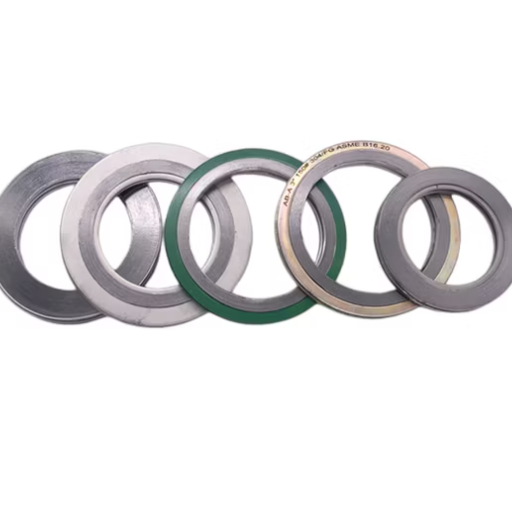

Semi-metallic gaskets combine the resilience of soft materials with the strength of metals, making them an excellent choice for situations needing either versatility or durability. Typically, they are made with a metallic core or winding (stainless steel being widely used) and a filler material (such as graphite or PTFE) to enhance the sealing performance. These gaskets are sometimes subjected to rather high temperatures and pressures and thus find uses in industries such as oil gas, petrochemical, and power generation. Additionally, their design permits them to yield to the flange surface, while a level of strength is maintained which guarantees sealing under varying operational conditions. Due to these abilities, semi-metallic gaskets are generally considered for more complex and critical sealing applications.
Characteristics of Semi-Metallic Gaskets
Semi-metallic gasket materials combine soft material resilience with metal strength to ensure high versatility and performance. A range of gaskets is designed for a broad spectrum of aggressive environmental conditions that include environments with high temperatures and pressures, among others, to name a few. These gaskets conform well to irregular flange surfaces, promoting a tight and reliable sealing. The durability and flexibility enable sealing to withstand centercut representations between operating parameters, considering an excellent option for critical applications.
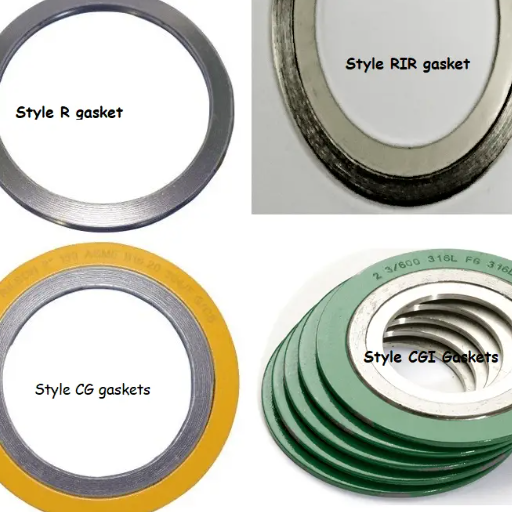
Common Types of Semi-Metallic Gaskets
| Gasket Type | Description | Best Application |
| Spiral Wound Gaskets | Combine sealing elements with metal affixations, giving excellent resiliency and adaptability | High-pressure and temperature environments |
| Kamprofile Gaskets | Consist of a metal core with a soft sealing layer | High-pressure environments and repeated use |
| Corrugated Metal Gaskets | Use metal with serrated or corrugated surfaces to up-seal performance | Lower bolt loads applications |
| Jacketed Gaskets | Consist of a soft filler material encased in a metallic outer shell | Heat exchangers and similar equipment |
Each of these types addresses a specific sealing challenge, making all of them reliable performers in a broad spectrum of industrial applications.
Performance Factors: Temperature and Pressure
Temperature and pressure form the essence of performance considerations when gaskets are to be chosen for industrial concerns. Situations involving high temperature require materials resisting thermal degradation; thus, metallic or composites will be used to form gaskets because they would retain their integrity with extreme heat. In a similar vein, gaskets used in systems with high pressures are expected to succumb before significant compressive forces, so that spiral-wound, or corrugated metal gaskets would preferably be used because of their robustness. Both instances must be analyzed simultaneously, given that situations toggling from one to the other can further incriminate the stress laid upon the gasket and cause its failure. Good material choice, with the design, will ensure that seals remain reliable with their performances changing with temperature and pressure.
Spiral Wound Gaskets
Spiral wound gaskets are engineered to resist an extensive array of guard pressures and temperature conditions effectively. These gaskets combine metal and filler materials for the purposes of imparting strength and resilience. The filler imparts sealing capability while the metal strength and durability. The selection of a spiral wound gasket must contemplate the working temperature; thus, for instance, graphite or PTFE are better for high-temperature applications. Regarding strength in compression, spiral wound gaskets are constructed to last through pressure fluctuations, due to good design and choice of metal, which for example can be stainless steel. Installation is an equally important factor if any gasket material and design is even to work well; this includes ensuring that no damage is done to flange surfaces prior to installation. By covering all such aspects, spiral wound gaskets shall give risk-free operation in any industrial application.
Construction of Spiral Wound Gaskets
Spiral wound gaskets feature both metal and filler design to maintain balance between strength and sealing ability. These are manufactured by winding a metallic strip, typically stainless steel or another suitable alloy, in a spiral manner along with a soft filler material, such as graphite, PTFE, or mica.
Key Components:
- Metal Strip: Provides structural integrity and compressive strength to the gasket
- Filler Material: Helps to conform the seal to flange surfaces in the face of temperature and pressure variations
- Outer Ring: Centers the gasket within the flange
- Inner Ring: Prevents inward buckling while protecting the softer filler material from chemical and thermal degradation
It can thus assert with confidence that its design is well suited for heavy-duty industrial applications.
Benefits of Spiral Wound Gaskets
- Excellent Sealing Performance: Maintain the integrity of the system under high-pressure and very high-temperature conditions
- Superior Resilience: Better resilience and adaptability of the seal to flange imperfections even under fluctuating scenarios
- Enhanced Durability: High level of durability, resistance to inward buckling, and protection from chemical and thermal degradation
- Operational Efficiency: Flexibility and dependability reduce maintenance efforts and increase operational efficiency
Applications in Flange Sealing
Spiral wound gaskets are fundamental to flange sealing since they resist harsh conditions. They are used extensively where high-pressure and high-temperature conditions exist, such as:
- Oil and gas processing
- Chemical processing
- Power generation
Their unique construction assures a leak-proof sealing even though they are put under extreme thermal cycling or vibration conditions. These gaskets are also trusted with sealing applications for corrosive or toxic fluids since the materials resist chemical degradation without losing either their integrity or performance. Their versatility and efficiency in a broad spectrum of industries make them best for achieving a reliable and durable flange seal.
Choosing the Right Gasket for Your Application

When selecting the ideal gasket for your application, it is crucial to consider the system’s requirements and operating conditions. Here are some critical considerations:
- Material Compatibility: The selected gasket must resist chemicals or other corrosive substances it will be in contact with. For instance, PTFE and graphite gaskets are the best suited in corrosive environments.
- Pressure and Temperature Limits: The type of gasket employed in the application must be designed to withstand the application maximum pressure and temperature so that it does not fail once put to use under severe conditions.
- Flange Type and Surface Finish: A gasket that corresponds with the flange type and the surface roughness as well for a solid and leak-free seal.
- Application-specific Considerations: This could include vibration, thermal cycling, and regulatory requirements such as FDA approved material for food or pharmaceutical use.
Key Takeaway:
It is in the best interest of performance, longevity, and safety that the gasket properties are matched with the specifications of your system. The best results will always come from following the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Factors to Consider: Flange Faces and Material Compatibility
While considering the flange faces and material compatibility, it is important to consider what types of flange face exist; it can be flat, raised, or even grooved, all of which will mandate the type of gasket and its design required for creating a reliable seal.
Material compatibility must be judged depending upon operating conditions, temperature, pressure, and chemical exposure, so it is assured that the gasket material can endure the exact environment so far without degradation or failure.
Moreover, think about dissimilar material combinations that are prone to galvanic corrosion, and always check if the selected materials conform to relevant industry standards or regulations concerning the intended application.
Understanding Gasket Material Properties
When selecting gasket materials, the major concerns are temperature, pressure, and chemical compatibility. PTFE gaskets, for instance, are great for very high temperatures and corrosive chemicals, whereas rubber gaskets are better for less severe environments.
It’s also important to check whether the materials comply with standards such as ASME or ASTM, depending on the application.
Other considerations include avoiding galvanic corrosion by not mixing dissimilar metals unless absolutely necessary and in those cases, checking for a coating or barrier that would work. Basically, materials that will do the job well under the actual operating conditions in terms of durability and compliance should be selected. If you follow these guidelines, you will basically guarantee the best performance of the gasket in any industrial application.
Summary of Gasket Selection Guidelines
- Always consider operating conditions such as temperature, pressure, and chemical exposure to guarantee suitability for the intended application
- Select materials that are approved by recognized standards, such as ASME or ASTM, for quality and reliability
- Dissimilar metals should be avoided unless absolutely necessary to reduce the risk of galvanic corrosion
- Protective coatings or barriers should be taken into consideration when necessary
- Material options should be prioritized that provide durability, reliable sealing performance, and conform to applicable standards so as to resist the specific requirements of the application
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are Semi-Metallic Gaskets and How Do They Compare to Spiral-Wound Gaskets?
A semi-metallic gasket is a hybrid gasket: it combines metallic and non-metallic components, allowing it to be used for diverse applications. Unlike the standard spiral wound gaskets where the main construction involves spiral winding of metal and filler material, the semi-metallic gaskets may use alternate materials such as flexible graphite for the very purpose of better sealing. The metal skeleton in semi-metallic gaskets supports them to work at high temperatures and pressures, and the thickness of these gaskets can also vary, thus giving ample choice for the flange faces and sealing requirements. Generally speaking, these gaskets find suitability in situations where the prevention of leakage is paramount.
What Materials are Used in Spiral-Wound Gaskets?
Spiral-wound gasket designs generally come in alternating layers of metal strips and layers of non-metallic filler material. The metal winding is imperative for strength, whereas the filler material serves to seal the gasket when put on compression. These gaskets can be made using several materials, both metallic and non-metallic, and these can be chosen as per the needs of a particular application. The use of materials like flexible graphite aids in improving sealing properties, especially under high-temperature setting. Moreover, a spiral-wound design comprises a feature where it is embossed with concentric rings to control leakage well.
What Types of Applications Utilize Jacketed Gaskets?
Jacketed gaskets with their soft element enclosed by a metal jacket find use in applications where an enhanced sealing feature is sought. The metal jacket provides strength and the soft material fills the irregularities of the flanges to seal well. As such, these are ideally suited for situations presenting the high risks of leakage associated with high pressure. Among other things, they find application in chemical processing, oil and gas, and power generation. The presence of metallic and non-metallic materials in jacketed gaskets provides the opportunity to modify them to meet specific operational requirements.
How Do Gasket Materials Affect Performance?
The performance of the gaskets depends largely on the materials used for their manufacture. Metallic gaskets show high strength and durability and, therefore, may be used under extreme temperature and pressures. On the other hand, non-metallic gaskets are suitable for applications that require almost perfect sealing against non-corrosive fluids. Semi-metallic gaskets stand in the middle, having some of the benefits of each group. The final compliment is offered by the filler material and the thickness of the gasket, which really dictates how well the gasket seals and how long it will stay in service.
References
-
My Reliable Power: This blog discusses the quietest generators, highlighting models like the Generac Guardian series with operational noise levels as low as 58 dBA. Source
-
Electric Generators Direct: A detailed resource on quiet standby generators, including the Generac Guardian® 22kW Standby Generator System. Source
-
Amazon Product Listing: Features the Oxseryn Portable Inverter Generator, a 2500W gas-powered generator known for its quiet operation and suitability for home backup. Source
- Top Semi-metallic Gaskets Suppliers in China
Ready to Select the Perfect Gasket?
Contact our technical team for expert guidance on choosing the right metallic gasket solution for your specific industrial application.






