In machinery, vehicles, construction and many other applications, particularly when there is a need to secure components, the use of fasteners is essential. From the diversity of materials like flange and regular nuts, which are popular choices, one can go either way since they all come with advantages and disadvantages. However, when it comes to selecting flange nuts over regular nuts, which will be appropriate for the application at hand? This article determines the differences between flange nuts and regular nuts and sheds light on the features, advantages and standard scenarios of application. Whether you’re a professional or beginner, grasping these aspects will help you reach correct outcomes and ensure the stability of your components.
Understanding Flange Nuts
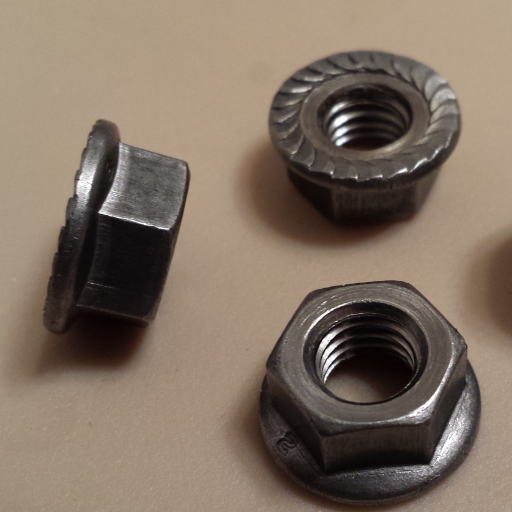

Flange nuts are a specialized type of nut used on bolts or screws to help distribute the load when tightening. These nuts consist of a flanged nut and washer that have been combined in one component, making them easy to use without additional hardware. Using flange nuts prevents loosening due to vibration and prevents surfaces from being damaged, eliminating the need to incorporate separate components like washers to save time and maintain a tight, stable joint.
Key Point: Flange nuts are known to be efficient and highly durable, making them indispensable for heavy-duty conditions and critical applications.
What is a Flange Nut?
A flange nut is best described as a fastening device with a wide flange that consists of an integral washer. The function of the flanged portion is to:
- Evenly distribute the pressure applied by the nut on the load-bearing surface
- Prevent damage to the material
- Ensure a firm grasp where multiple pieces are utilized
- Withstand extraordinary forces in systems requiring self-locking capabilities
Flange nuts frequently come in two main design variations:
- Serrated flange nuts: Feature a textured surface to prevent loosening from vibrations
- Flat flange nuts: Have a smooth surface, typically used where surface protection is the priority
These nuts are available in various materials including steel, stainless steel, and nylon, each providing different characteristics like resistance to wear, temperature, and corrosion.
Features of Flange Nuts
| Feature | Benefit | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Integrated Washer Design | Distributes load evenly, prevents material damage | All fastening applications |
| Serrated Grip | Prevents loosening from vibrations | Automotive and machinery |
| Material Versatility | Suits various environments and conditions | Indoor/outdoor, marine applications |
| Corrosion Resistance | Long-lasting performance in harsh conditions | Outdoor and industrial use |
| Assembly Efficiency | Eliminates need for separate washers | High-volume manufacturing |
Key Features Breakdown
- Load Distribution: The integrated flange acts like a washer, distributing load evenly across surfaces
- Enhanced Grip: Serrated flanges grip materials to reduce loosening from vibrations
- Material Options: Available in carbon steel, stainless steel, and nylon for different environments
- Temperature and Corrosion Resistance: Specialized coatings provide protection in harsh conditions
- Streamlined Assembly: Eliminates the need for separate washers, saving time and components
- Standard Compliance: Available in ANSI, DIN, and ISO standard sizes
- Industry Versatility: Used across automotive, construction, aerospace, and heavy machinery sectors
Applications of Flange Nuts
Flange nuts enjoy versatility across numerous industries and applications:
Automotive Applications
- Engine components subjected to frequent vibrations
- Suspension systems
- Chassis and body panel connections
Construction and Heavy Machinery
- Structural connections requiring durability
- Equipment mounting points
- High-stress joint applications
Industrial Applications
- Manufacturing equipment
- Conveyor systems
- Heavy-duty machinery connections
Comparing Flange Nuts vs. Regular Nuts
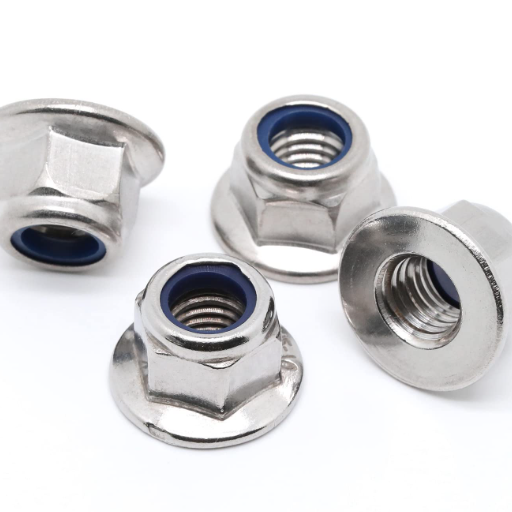

While both flange nuts and regular nuts serve the fundamental purpose of securing bolts and components, their designs and applications vary significantly.
| Aspect | Flange Nuts | Regular Nuts |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Built-in washer-like flange at base | Simple design, requires separate washers |
| Load Distribution | Even distribution across larger surface area | Concentrated load (unless washer used) |
| Vibration Resistance | Superior resistance to loosening | May require additional locking mechanisms |
| Assembly Time | Faster (no separate washer needed) | Slower (requires washer installation) |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Applications | High-stress, high-vibration environments | General-purpose, low-stress applications |
Design Differences
The primary distinction between flange nuts and regular nuts lies in their structural design:
- Flange Nuts: Feature an integrated washer at the base, providing improved load distribution and eliminating the need for additional washers
- Regular Nuts: Simple and versatile design that often requires separate washers to achieve similar load distribution
Performance and Strength
Flange nuts excel in applications requiring high performance and strength under heavy stresses:
- Distribute load over larger areas to prevent material damage
- Remain securely fixed under heavy vibrations
- Reduce the need for additional components
- Allow for smoother assembly without compromising strength
Cost Considerations
When evaluating cost, consider both initial investment and long-term value:
- Initial Cost: Flange nuts have higher upfront costs than regular nuts
- Component Savings: Built-in washer design eliminates need for separate washers
- Assembly Savings: Reduced installation time and labor costs
- Long-term Value: Superior durability reduces replacement and maintenance costs
Types of Flange Nuts
Hex Flange Nuts
Hex flange nuts are versatile and reliable fasteners featuring:
- Hexagonal shape for easy tightening with standard tools
- Flange that spreads pressure evenly across larger surface areas
- Prevention of loosening due to vibrations
- No requirement for specialized installation tools
- Excellent choice for both professionals and DIY applications
Serrated Flange Nuts
These specialized nuts feature serrations on the flange surface that provide:
- Locking action that prevents loosening from vibration
- Serrations that bite into mating surfaces for additional security
- Elimination of washer requirements during installation
- Time and effort savings during assembly
- Ideal use in automotive, machinery, and construction applications
Lock Nuts and Locknuts
Lock nuts are specialized fasteners designed to resist loosening through:
- Nylon inserts for thread locking
- Deformed threads for mechanical interference
- Additional locking elements for enhanced security
- Reliable performance in high-vibration environments
- Applications in automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery
Choosing the Right Fastener

Optimal fastener selection requires careful assessment of multiple factors:
Key Factors to Consider
- Load Requirements: Determine the type and magnitude of loads the fastener will experience
- Environmental Conditions: Consider temperature, moisture, chemicals, and corrosive elements
- Vibration Exposure: Assess the level of vibration the assembly will encounter
- Material Compatibility: Ensure compatibility to prevent corrosion and degradation
- Strength Grade: Match fastener strength to mechanical demands
- Thread Specifications: Verify thread type, length, and diameter for proper fit
- Special Features: Consider lock nuts or adjustable screws for specific needs
When to Use Washers
Washers should be used to:
- Improve the performance and reliability of fastened joints
- Reduce friction and vibration effects
- Distribute loads to protect surface materials
- Protect softer materials from damage
- Provide additional stability and corrosion resistance
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Material Mismatch: Choosing washers without considering material or load requirements
- Wrong Washer Type: Using plain washers where lock washers are needed for high-vibration applications
- Over-tightening: Excessive torque that deforms washers or damages bearing surfaces
- Environmental Neglect: Failing to consider corrosion or contamination factors during installation
Inadequate Planning: Not analyzing all factors before fastener selection
References
-
Nuts & Bolts Lesson – Purdue University
This document provides insights into different types of nuts and bolts, including their applications and characteristics. -
EML2322L Fastener Reference Guide – University of Florida
A comprehensive guide on fasteners, including bolts, screws, and nuts, detailing their differences and uses. -
ISO Flanges – Cornell University
This resource discusses flange types and their fastening methods, including the use of nuts and bolts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What’s the difference between a flange nut and a regular nut?
The primary difference between a flange nut and a regular nut lies in the design and functionality. A flange nut, or serrated flange nut, features a built-in washer that provides a larger bearing surface. This design helps distribute the load and provides a tight fit, making it ideal for applications where the nut might be subjected to vibration or movement. In contrast, a regular nut lacks this flange and may not perform as effectively in preventing loosening. Additionally, flange nuts can be used in conjunction with oversized holes, offering versatility in various applications. Overall, the built-in washer in flange nuts enhances their performance compared to standard nuts.
How do locknuts differ from flange lock nuts?
Locknuts and flange lock nuts serve similar purposes in preventing loosening, but they differ in design. A locknut typically uses a prevailing torque mechanism to resist loosening, while a flange lock nut incorporates a serrated face that grips the surface beneath it. This serrated flange acts as a built-in washer, increasing the contact area and enhancing stability. Locknuts are often used in conjunction with standard nuts to secure threaded fasteners, while flange lock nuts provide a more robust solution for applications prone to vibrations. Both types are effective, but the choice depends on the specific demands of the application.
Can serrated flange nuts be reused?
Serrated flange nuts can often be reused, but their effectiveness depends on the condition of the nut and the surface it mates with. If the serrated face and the flange are still intact and the coating on the mating surface is not damaged, they can provide a tight fit when reused. However, it is crucial to inspect them for any signs of wear or deformation that might affect their performance. Reusing nuts and flange nuts can save time and money, provided they are still in a proper manner for use. Always ensure that they are retorqued appropriately to maintain bolt tension in applications.
What are the advantages of using a hex nut over a flange nut?
Hex nuts and flange nuts each have their advantages depending on the application. Hex nuts are versatile and widely used in many applications due to their simple design and ease of installation. They can be tightened with standard tools and are suitable for many types of threaded fasteners. However, flange nuts offer a larger surface area, which can resist loosening better in environments with vibration. If the application involves oversized holes or requires a secure fit, flange nuts may be the better choice. Ultimately, the decision between using a hex nut or a flange nut should be based on the specific requirements of the project.
In what scenarios are nuts and flange nuts used together?
Nuts and flange nuts can be used together in scenarios that require additional security and stability. For instance, in heavy machinery or automotive applications, a flange nut may serve as the primary fastening component, while a regular nut can be used to further secure the assembly. This combination can help ensure that the fastener remains tight even under high-stress conditions. Additionally, using both types allows for adjustments in bolt tension without compromising the integrity of the joint. In certain applications, this method can provide a better preload and resist loosening more effectively than using either type alone.






